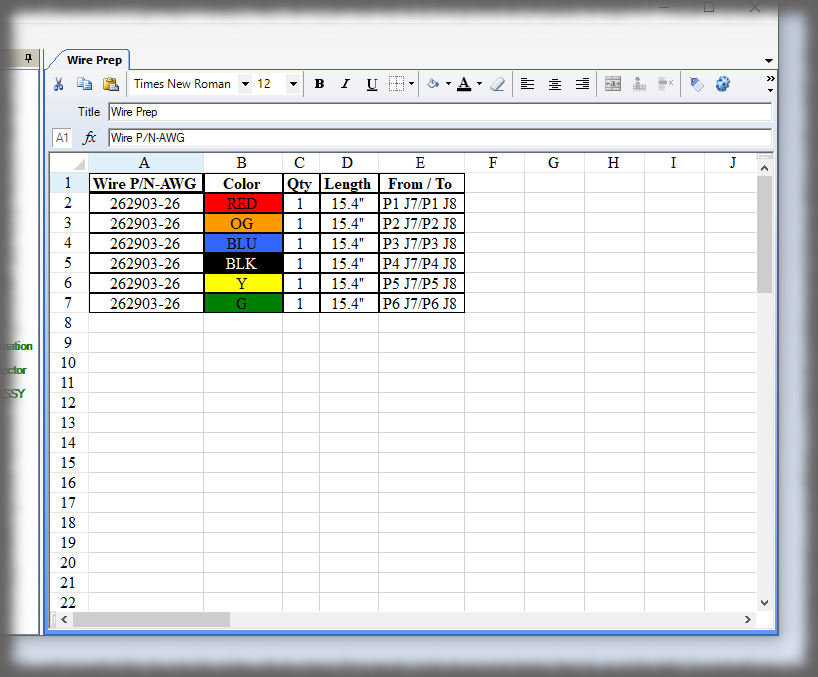
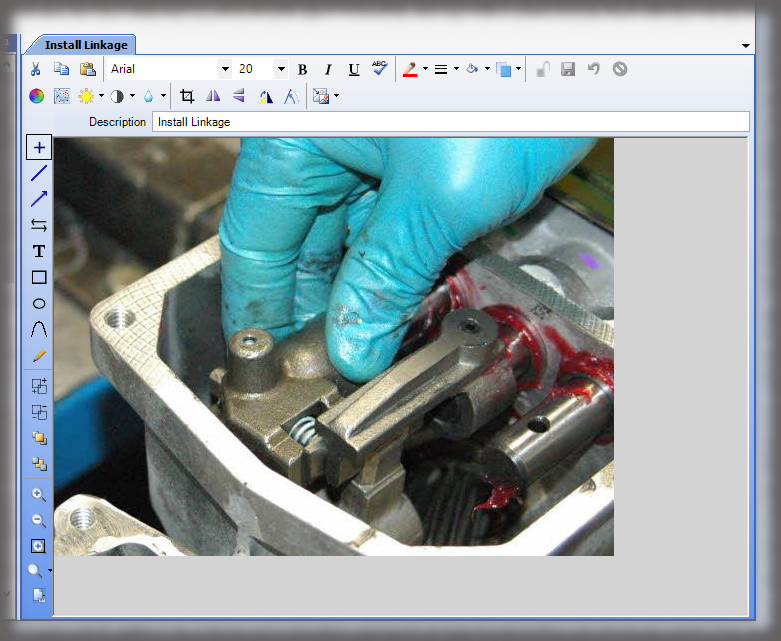
In a manufacturing sector that is seemingly dominated by automation and robotics, a surprising trend has emerged in 2023—the resurgence of manual assembly. Why is manual manufacturing on the rise? While automation certainly provides numerous benefits, such as increased efficiency and precision, there are certain scenarios where manual assembly is superior or necessary. The resurgence is driven by several factors, including customization demands, flexibility requirements, and a renewed focus on craftsmanship and human skills. Here are the reasons behind the resurgence of manual assembly in the US and the impact it is having on the manufacturing industry.
1) Customization Demands
While automation is excellent at producing large quantities of standardized products efficiently, it often struggles to handle customization. But competition drives innovation. For example, lean manufacturing paved the way for car manufacturers to allow customers to change details of their customized car up to hours or days before the car is assembled.
One of the primary drivers behind the resurgence of manual assembly is the growing demand for customized products. Customers are looking for unique, personalized products that cater to their needs and preferences, and manual assembly offers the flexibility and adaptability that automation cannot match. Skilled, human workers easily switch between tasks and make adjustments on the fly to accommodate custom details of an order. Configurability drives the competitive advantage for manufacturers in various industries, from automotive to electronics.
2) Flexibility Requirements
Manufacturing processes are increasingly dynamic and complex. Market demands are constantly shifting, and manufacturers need the agility to adapt quickly to these changes. For example, during Covid there were manufacturers changing engineering designs when certain critical parts were no longer available due to supply chain problems. Manual assembly provides a level of flexibility that automated systems struggle to achieve. This is particularly important in industries where product lifecycles are short, and frequent reconfiguration is necessary.
Manual assembly also supports reconfigured production areas to accommodate different product variants or production volumes. Workers can be trained to handle various tasks and switch between them as needed. This adaptability allows manufacturers to respond rapidly to changing market conditions and remain competitive.
3) Craftsmanship and Quality
In an era where mass production and automation often prioritize speed and quantity, the resurgence of manual assembly signifies a renewed emphasis on craftsmanship and quality. Skilled manual workers bring a level of precision and attention to detail that is challenging for automated systems to replicate.
Consumers are increasingly discerning, valuing products that showcase quality and attention to detail. Manual assembly allows manufacturers to meet these demands and ensure each product is assembled with care and precision. This often results in higher-quality products that command premium prices in the market.
4) Complex and Niche Markets
Certain industries and market segments require specialized products that are produced through intricate assembly processes. These products often serve niche markets where precision and traceability are important. Manual assembly facilitates the fine-tuning of production processes to meet the specific requirements of those markets.
For example, in the aerospace industry, where safety and precision are critical, manual assembly is still prevalent for assembling complex components. Similarly, in the production of high-end musical instruments, skilled craftsmen are essential to achieve the desired sound and quality. In these markets, manual assembly is not just a preference but a necessity.
5) Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices is another defining trend of 2023. Environmental concerns, coupled with regulatory pressures and consumer demand for eco-friendly products, are driving manufacturers to adopt greener processes in the production of their goods.
Many companies are investing in renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, to power their operations. There is also a greater emphasis on recycling and reducing waste in production processes and advanced materials, like bioplastics, are being incorporated into designs to reduce the environmental impact. Manual assembly is another way that companies are reducing their carbon footprint–replacing automated machines that emit pollutants with a pair of hands.
6) Job Creation and Local Manufacturing
The resurgence of manual assembly has the potential to create jobs and promote local manufacturing. In regions where unemployment is a concern, investing in skilled manual labor can have positive economic impacts. It also reduces the dependency on imported goods, fostering local self-sufficiency.
Furthermore, the “Made in [Country]” label is gaining importance as consumers become more conscious of the origin of products. Manual assembly can help manufacturers meet local production requirements and tap into the growing demand for domestically produced goods.
Navigate Manufacturing Changes with Sequence
While automation and robotics continue to play a vital role in modern manufacturing, the resurgence of manual assembly in 2023 highlights the enduring value of human skills and adaptability. A balanced approach that combines the strengths of automation and manual assembly can lead to improved competitiveness and better alignment with market demands.
Contact Sequence Software today to learn more about how a robust system for creating, managing and deploying electronic work instructions facilitates the return to manual assembly in the US.